LEI stands for Legal Entity Identifier, and it is a unique code assigned to all registered legal entities that intend to do financial transactions on the international level. This unique code has a structure that is defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 17442 standard.
You can view the full publication of LEI of ISO standard at ISO 17442:2019
Every set of characters in this code has a meaning attached to them, so they are not randomly generated characters as most people might think. In this article, we will help you understand the structure of a legitimate LEI code to make it easy for you to interpret it once you come across one.
Attributes of an LEI code
-
It is unique: Any specific LEI code belongs to only one entity and cannot be issued to another. If you come across any two companies with a similar LEI code, it simply means one of these two is not legitimate. You can validate any LEI code to verify its authenticity.
-
It is an international standard: An LEI code is recognized internationally, so it can be used to identify your entity in any part of the world.
-
An LEI code is a public good: Unlike some other registration details of an entity, an LEI code is available for the public to view. Once an entity is registered into the Global Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) System, its LEI code is published right away for the entire public to see. The information published alongside this code includes; the official name of the legal entity, its registered address, country of formation, the date of the first LEI assignment, date of the last update of the LEI information, and the expiry date of the current one (if applicable). You can look up any LEI in our LEI database.
-
An LEI code is supported by quality data: Besides the code itself, all the basic information about the company is published along with the code.
Code Structure of a Legal Entity Identifier
An LEI code is a unique code with 20 characters that contains numbers and letters of the alphabet. To show how an LEI code looks like, here is the LEI code of Apple Inc; HWUPKR0MPOU8FGXBT394.
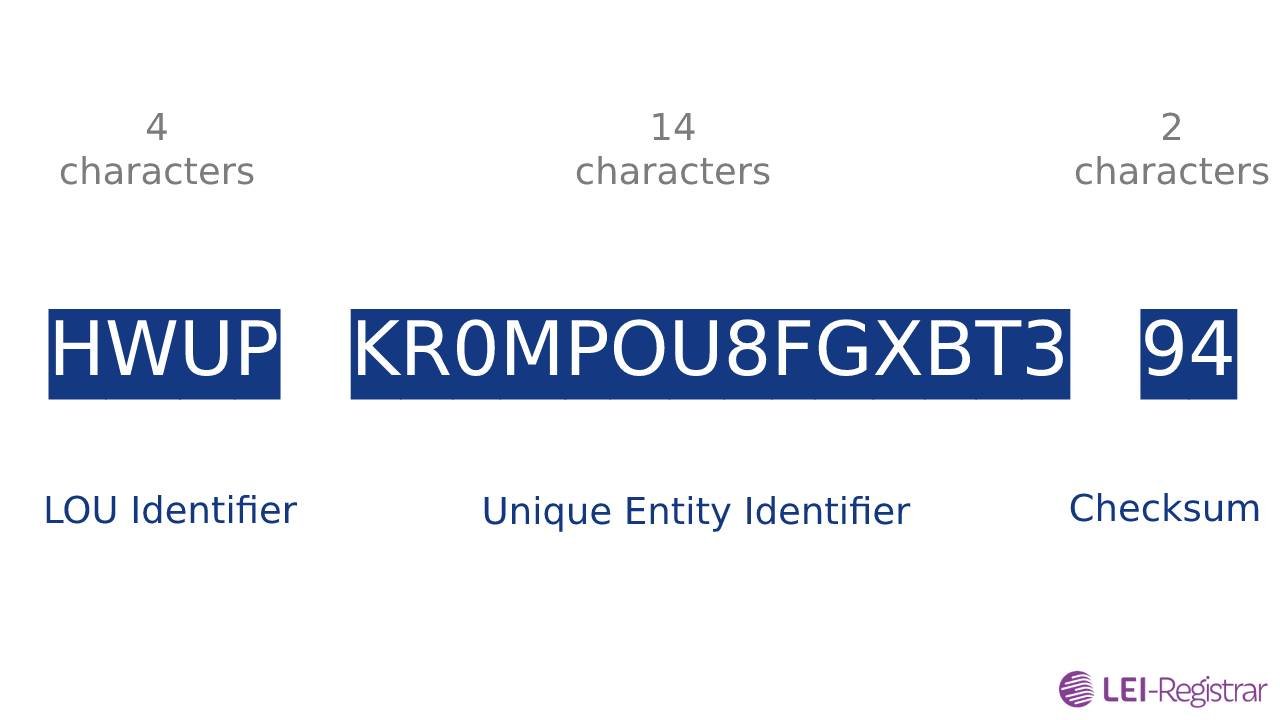
So, what do these characters in the code represent?
- The first four characters: Represent the Local Operating Units (LOU) that issues the LEI code to the company. This is to ensure uniqueness among codes issued by the same LEI issuer.
- Character 5 to 18: These characters represent a unique alphanumeric string issued to an organization by the LOU. So, this string of characters cannot be the same for entities under the same LOU.
- The last 2 characters: Represent the checksum digits. These are calculated using the ISO 7064 MOD 97-10 algorithm and can be verified with our LEI validator.
Need to validate multiple codes at once? Try our Bulk LEI Validator.
If you still have more questions, please refer to our What is LEI code? guide.